The inspection checklist is a beacon of meticulous oversight in today’s complex professional landscape. Revered for its systematic approach, it has become an indispensable instrument, ensuring that industries across the board maintain the highest standards of quality and safety. Delving into its intricacies reveals a set of criteria and a comprehensive framework that empowers businesses to consistently deliver excellence.
This guide offers a deep dive into the foundations and applications of the inspection checklist, elucidating its significance through practical examples and presenting templates tailored for precision. Join us as we navigate the nuances of this pivotal tool, underscoring its pivotal role in shaping industry best practices.
What’s Inspection Checklist? Definition
An inspection checklist is a comprehensive document or tool, utilized primarily in examining specific items, processes, or facilities to ensure compliance with set standards. It is systematically organized and designed to aid inspectors in identifying potential issues, ensuring consistency in the inspection process. Each item on the checklist represents a specific criteria that needs to be checked or verified. The purpose of such checklists is to ensure that no critical elements are overlooked during inspections.
The inspection checklist helps maintain the quality and safety of products, services, or operations by providing clear standards and expectations. Depending on their application, these checklists can be tailored for various sectors such as construction, manufacturing, or services. Typically, the checklist contains boxes or spaces for ticking off or noting observations. Once completed, it provides a tangible inspection record, which can be reviewed for compliance or improvements. Ultimately, an inspection checklist serves as both a guide for inspectors and a benchmark for what’s being inspected.

Why Are Inspection Checklists Important?
Inspection checklists are of paramount importance for several reasons:
- Consistency and Uniformity: They ensure every inspection is performed consistently, reducing the chances of missing or overlooking crucial details. This uniformity is vital when multiple inspectors are involved, ensuring everyone adheres to the same standards.
- Efficiency: With a well-structured checklist, inspectors can carry out their tasks more swiftly and methodically, saving time and resources.
- Comprehensive Review: A checklist examines every critical component or aspect. This is especially important in complex environments where forgetting a single aspect can have significant consequences.
- Documentation and Accountability: Completed checklists serve as a record of the inspection. This documentation can be useful for audits, reviews, or verifying that standards were upheld. It also promotes accountability among inspectors.
- Training Tool: For new inspectors or staff, checklists serve as a training guide, ensuring they understand and cover all necessary areas during an inspection.
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying and addressing potential issues or non-compliances early on, checklists help in reducing risks, preventing potential accidents, and avoiding regulatory fines.
- Quality Control: They play a crucial role in ensuring quality standards. Whether in manufacturing, construction, or any other sector, maintaining quality is often tied to following a specific set of criteria, which checklists can delineate.
- Enhanced Communication: Checklists can facilitate better communication between departments or stakeholders. They clearly show what’s been inspected, what passed, and where issues might exist.
- Continuous Improvement: As gaps or recurrent issues are identified through checklists, organizations can focus on these areas for improvement, refining processes or protocols accordingly.
- Customer and Stakeholder Trust: Demonstrating adherence to standardized inspection protocols can boost the confidence of customers, stakeholders, or regulatory bodies in an organization’s commitment to quality, safety, and excellence.
In summary, inspection checklists are essential for upholding quality, ensuring safety, and maintaining consistency across various domains. They bridge theoretical standards and practical implementation, ensuring processes align with their intended design and purpose.

Basic Features And Uses Of An Inspection Checklist
An inspection checklist, though simple in its appearance, is underlined by various features that make it an indispensable tool in various sectors. Here are some of the basic features and their associated uses:
Features of an Inspection Checklist:
- Structured Format: An inspection checklist is organized systematically, often broken down into sections or categories, ensuring a logical inspection flow.
- Clear Criteria: Each item or point in the checklist denotes a specific standard or criteria that needs verification, ensuring the clarity of what is to be inspected.
- Tick Boxes or Spaces: These allow inspectors to mark whether a specific item meets the set standard or requires further attention.
- Notes Section: Many checklists allow inspectors to jot down additional observations or details about a particular item.
- Priority Indicators: Some checklists might highlight certain items as ‘high priority’, indicating their critical importance in the inspection process.
- Reference Numbers or Codes: For complex inspections, each item might have a reference number linking it to a more detailed set of standards or procedures.
- Responsive Design: Modern digital checklists are designed for various devices, including tablets and smartphones, allowing for real-time updates and easy sharing.
- Attachment Features: In digital checklists, there’s often an option to attach images or documents to provide visual evidence or further context.
Uses of an Inspection Checklist:
- Quality Assurance: To ensure products, services, or operations meet established quality standards.
- Safety Audits: For examining the safety protocols of facilities or operations, ensuring no breach could lead to accidents or injuries.
- Regulatory Compliance: To ensure operations adhere to industry-specific regulations, laws, and standards.
- Operational Maintenance: For periodic machinery, equipment, or facilities checks to guarantee optimal working conditions.
- Onboarding & Training: They guide new employees to familiarize them with company protocols, standards, and best practices.
- Inventory Control: For verifying inventory items’ quantity, condition, and organization.
- Environmental Audits: To ensure businesses or processes align with environmental standards and aren’t harming the environment.
- Customer Service: For assessing the quality of service provided to customers, ensuring it meets or exceeds company standards.
- Facility Management: To evaluate the state of buildings, grounds, and associated services for maintenance and improvement.
- Documentation & Record Keeping: As a tangible record of inspections, they can be stored and reviewed for audits or performance evaluations.
The versatility of inspection checklists and their structured design makes them a preferred choice in various sectors and scenarios, ensuring standards are consistently met and maintained.

Different Examples Of Inspection Checklists
Inspection checklists are utilized across various industries, each tailored to specific requirements. Here are different examples of inspection checklists based on their application:
Manufacturing Process Inspection:
- Verification of raw material quality.
- Examination of machinery for proper calibration.
- Checks on safety measures around machinery.
- Quality control of finished products.
Vehicle Maintenance and Safety:
- Brake system inspection.
- Verification of tire pressure and tread depth.
- Engine and transmission checks.
- Examination of lights and signals for proper functioning.
Construction Site Safety:
- Evaluation of protective gear usage (helmets, vests).
- Verification of scaffoldings for stability.
- Checks on electrical wiring and equipment.
- Inspection of tools and machinery for safety compliance.
Real Estate/Home Inspection:
- The structural integrity of the property.
- Verification of electrical systems.
- Examination of plumbing and water systems.
- Checks on insulation and ventilation.
Food and Restaurant Inspection:
- Examination of food storage areas for proper temperature.
- Verification of kitchen cleanliness.
- Checks on food handling and preparation methods.
- Inspection for pest control measures.
Retail Store Audit:
- Merchandise display and organization checks.
- Verification of safety protocols (e.g., fire exits).
- Examination of storage areas.
- Checks on staff adherence to company guidelines.
Environmental Impact Inspection:
- Monitoring waste disposal methods.
- Verification of emission controls.
- Examination of resource consumption (water, energy).
- Evaluation of measures to protect local ecosystems.
Warehouse and Inventory Audit:
- Verification of stock count.
- Examination of storage conditions.
- Inspection of security measures.
- Evaluation of dispatch and receiving processes.
Aircraft Maintenance Inspection:
- Verification of engine function and performance.
- Checks on electronic and navigation systems.
- Examination of the landing gear.
- Evaluation of cabin safety measures.
These are just a few examples, but they illustrate the vast range of applications for inspection checklists. Each checklist’s exact items and criteria will vary depending on industry standards, regulatory requirements, and specific operational needs.

How To Make An Effective Inspection Checklist?
Creating an effective inspection checklist tailored for inspection tasks requires a blend of thoroughness, clarity, and user-friendly design. Here’s how you can craft one:
- Determine the Scope: Clearly define what the inspection will cover. For example, is it for a facility’s overall safety, a product’s quality, or machinery maintenance?
- Gather Information: Collect existing standards, regulations, and best practices related to the inspection. This helps ensure your checklist aligns with recognized benchmarks.
- Engage Experts: Consult with experienced inspectors, stakeholders, or industry specialists. Their insights can guide what to include or prioritize in the checklist.
- Be Clear and Concise: To avoid ambiguity, each item should be worded clearly. Be concise to ensure quick comprehension during inspections.
- Categorize: Organize the checklist into logical sections or categories. This structure aids inspectors in systematically navigating the checklist.
- Prioritize Critical Items: Highlight or sequence the items based on their importance or risk factor, ensuring high-priority elements are not overlooked.
- Include Visuals: Whenever applicable, use symbols, diagrams, or reference images. Visual aids can offer clarity, especially in complex inspections.
- Provide Space for Annotations: Inspectors should have room to jot down specific findings, deviations, or additional observations related to each item.
- Pilot the Checklist: Before formalizing the checklist, test it in real-world inspections. This trial run can reveal gaps or redundancies.
- Iterate and Refine: Based on feedback from the pilot phase and continuous usage, make necessary modifications to improve the checklist’s efficacy.
- Ensure Accessibility: Inspectors should be able to access and utilize the checklist easily. Consider digital formats for flexibility, real-time updates, and integration with other tools.
- Review and Update: As processes evolve and standards change, the checklist should be periodically reviewed and updated to remain relevant and effective.
- Training: Ensure inspectors are adequately trained on using the checklist and what to look for in each item, especially if new or revised checklists are introduced.
- Feedback Mechanism: Establish a way for inspectors to provide feedback or suggest improvements to the checklist, fostering continuous refinement.
- Documentation: Consider including a section or mechanism for inspectors to formally sign off or verify the completion of the inspection, reinforcing accountability.
By crafting a thoughtful, well-structured inspection checklist, organizations can improve the consistency and quality of their inspections, ultimately enhancing safety, compliance, and operational excellence.

What Is Safety Checklist Inspections?
Safety checklist inspections refer to systematic evaluations to identify potential safety hazards in a given environment, system, or process. These inspections aim to prevent accidents and injuries and ensure the well-being of individuals by ensuring that all safety protocols, standards, and regulations are followed.
Purpose:
The primary goal of safety checklist inspections is to safeguard individuals, whether they are employees, customers, or the general public. These inspections ensure compliance with established safety regulations, standards, and best practices, minimizing the risk of accidents or injuries.
Components:
Safety checklists comprise specific items or criteria that need to be verified. Each item corresponds to a particular safety standard or protocol. The criteria might include verifying the proper functioning of safety equipment, adherence to safety procedures, or the safe condition of physical space.
Usage:
Safety checklist inspections can be used across various industries and settings:
- Industrial and Manufacturing Plants: Check machinery safety, protective gear usage, and emergency response measures.
- Construction Sites: To verify scaffold stability, use helmets and safety harnesses, and ensure hazard communication.
- Healthcare Facilities: To ensure the cleanliness of surgical tools, adherence to patient safety protocols, and proper storage of medications.
- Offices: To check ergonomics, fire safety protocols, and electrical safety.
- Transportation: Inspect vehicle maintenance, driver training records, and emergency preparedness.
- Educational Institutions: To verify the safety of play equipment, laboratory safety measures, and emergency evacuation plans.
Documentation:
After conducting the safety inspection, findings are documented. This documentation provides a tangible record, which can be used for further analysis, tracking improvements over time, and demonstrating compliance to external agencies or auditors.
Follow-up:
Safety checklist inspections are about identifying issues and taking corrective actions. Once potential hazards are identified, appropriate measures are implemented to mitigate them. Re-inspections may occur to ensure that corrective actions are effective.
Frequency:
The frequency of safety checklist inspections can vary based on the industry, nature of operations, and regulatory requirements. Some inspections might be daily, while others could be weekly, monthly, or annually.
Safety checklist inspections are a proactive approach to ensuring a safe environment. By systematically identifying and addressing potential hazards, these inspections play a pivotal role in accident prevention and the overall well-being of individuals.
Different Inspection Checklists Templates
Inspection checklist templates provide a structured format to help users systematically conduct assessments. Here are different inspection checklist templates based on various domains:
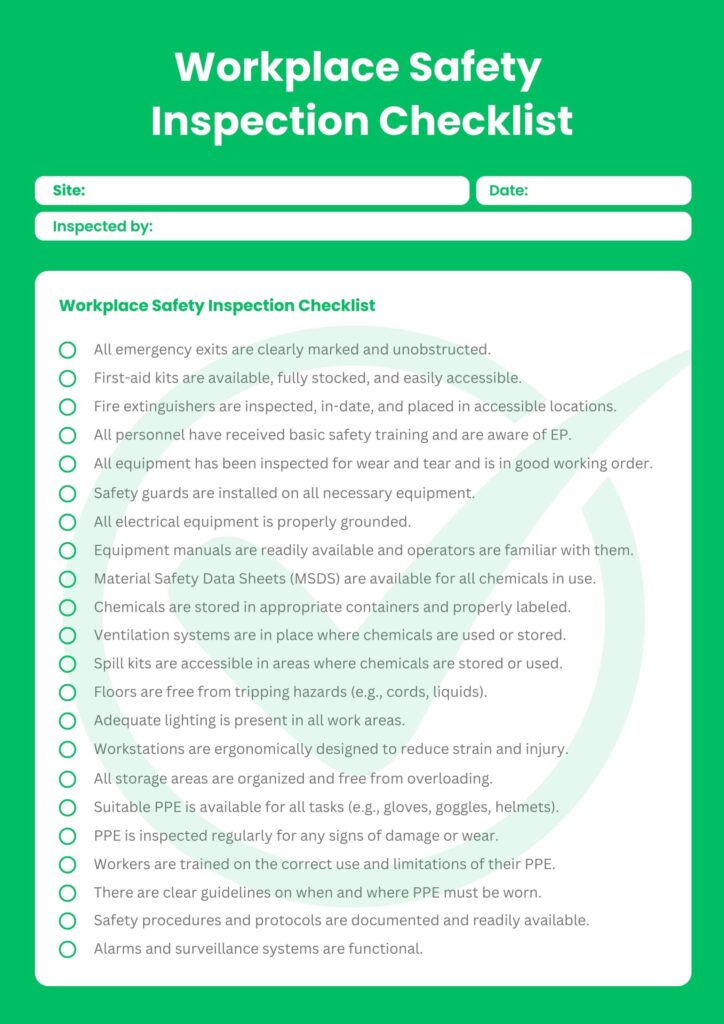
Workplace Safety Inspection Checklist Template
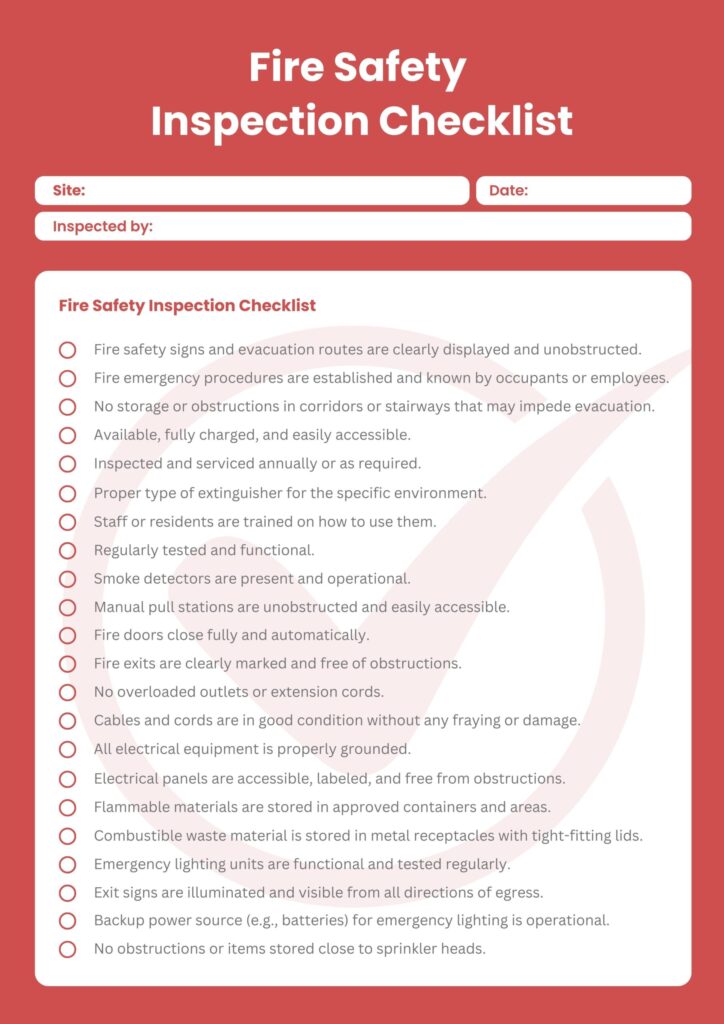
Fire Safety Inspection Checklist Template
Conclusion
The inspection checklist is more than just a list—it guides professionals toward consistency, excellence, and safety in their respective domains. Whether in manufacturing, IT, healthcare, or any other sector, these structured evaluations serve as the backbone of quality assurance, facilitating streamlined processes and reducing the potential for oversight.
Through real-world examples, we’ve seen its versatility and adaptability, while the provided templates offer a starting point for any organization or individual seeking to harness its benefits. In essence, the inspection checklist is not just a tool but a testament to the commitment to excellence, ensuring that standards are met, expectations are surpassed, and operations run smoothly.

