Injuries can happen anytime—at home, in the workplace, or on the road. While some incidents leave you with just a few scrapes or soreness, others can have life-altering consequences. But how do you know whether your injury is minor or major? And why does that distinction matter?
Recognizing the difference between major and minor injuries is essential for your health and navigating insurance claims, legal rights, and recovery options. Whether you’re dealing with a painful sprain or a traumatic brain injury, the severity of your injury determines how you recover, who’s responsible, and what kind of compensation you may be entitled to.
This comprehensive guide will explore what qualifies as a major or minor injury, how even small injuries can escalate, when to seek medical attention, and the legal implications you need to know. If you’ve been injured in an accident, this article will help you make informed decisions for your health and future.
What Is an Injury?
An injury is any form of physical harm or damage inflicted on the body due to accidents, trauma, or overuse. Injuries can be:
- Acute: Sudden onset due to trauma (e.g., fractures, sprains, concussions)
- Chronic: Gradual development due to repetitive stress or overuse (e.g., tendonitis, stress fractures)
Regardless of how they occur, understanding the severity of an injury is key to appropriate treatment and recovery.
What Are Minor Injuries?
Minor injuries are non-life-threatening and usually heal with minimal medical intervention. While they may cause discomfort, they rarely lead to long-term disability or major disruption in daily life.
Common Minor Injuries Include:
- Cuts and scrapes
- Bruises (contusions)
- Muscle strains or mild sprains
- First-degree burns
- Headaches and mild concussions
- Whiplash
- Minor back pain
- Small blisters
- Foreign object in the eye (dust, dirt)
Characteristics of Minor Injuries:
- Short recovery time (days to a few weeks)
- Often treated with first aid or outpatient care
- Rarely require hospitalization or surgery
Note: Even seemingly minor injuries can become serious if left untreated. Always monitor symptoms and consult a doctor if pain persists or worsens.
What Are Major Injuries?
Major injuries are more severe, often requiring immediate medical attention, extended recovery time, and specialized treatment. These injuries can be life-threatening, lead to permanent disability, or significantly affect a person’s quality of life.
Common Major Injuries Include:
- Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs)
- Spinal cord injuries
- Fractures and broken bones
- Disfigurement or severe burns
- Amputations
- Organ damage or internal bleeding
- Eye injuries leading to vision loss
- Crush injuries
- Paralysis or loss of mobility
Characteristics of Major Injuries:
- Require emergency care or surgery
- Often involves long-term rehabilitation
- May cause permanent impairment or chronic pain
- Significant impact on daily functioning and mental health
Example: A broken rib may seem minor, but if it punctures a lung, it becomes a major medical emergency.
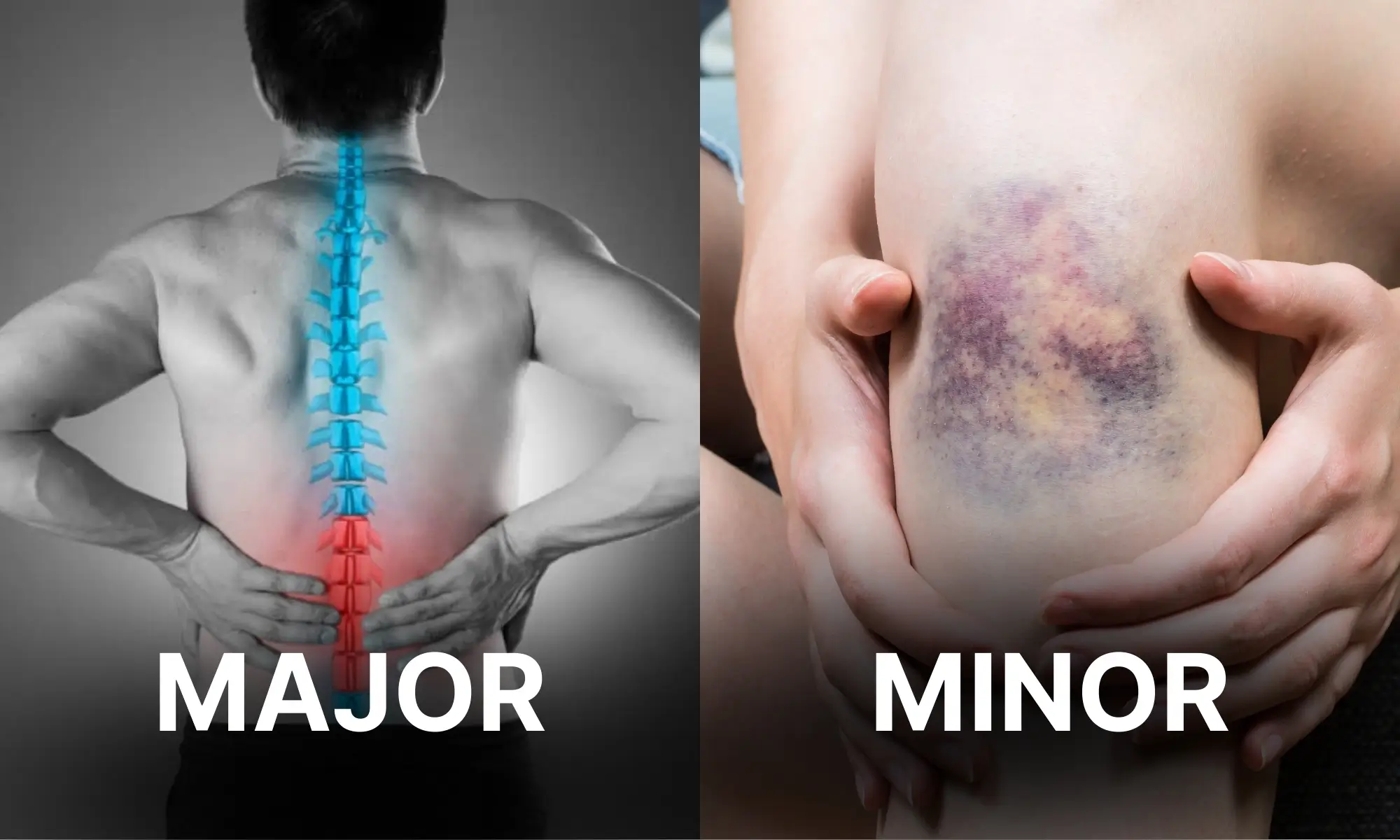
Key Differences Between Major Injuries and Minor Injuries
| Aspect | Minor Injuries | Major Injuries |
|---|---|---|
| Severity | Mild to moderate; not life-threatening | Severe; may be life-threatening or cause permanent damage |
| Examples | Bruises, small cuts, mild sprains, first-degree burns, headaches | Fractures, spinal cord injuries, traumatic brain injuries, amputations, deep burns |
| Medical Attention | Often treated with basic first aid or outpatient care | Requires emergency care, surgery, or long-term medical treatment |
| Recovery Time | Short-term (days to a few weeks) | Long-term (months to years); may involve permanent disability |
| Impact on Daily Life | Minimal disruption; can usually continue normal activities | Major disruption; may limit mobility, work, or independence |
| Legal and Compensation Claims | Often covered by basic insurance or personal injury protection | Higher compensation claims due to medical bills, lost wages, and long-term effects |
| Documentation Requirements | Detailed records, expert opinions, and ongoing treatment plans are often required | Detailed records, expert opinions, and ongoing treatment plans often required |
Summary:
- Minor injuries are typically non-critical, heal quickly, and don’t drastically affect your lifestyle.
- Major injuries are serious, often require complex medical care, and can have a lasting impact on your physical, emotional, and financial well-being.
Understanding this distinction is crucial for making informed medical, personal, and legal decisions after an accident or injury.

From Minor to Major: When Injuries Escalate
Not all serious injuries start out looking serious. In fact, many major health issues begin as minor injuries that are underestimated or left untreated. What seems like a small bump, ache, or bruise today could become a long-term or even life-threatening problem tomorrow.
How Minor Injuries Can Escalate
- Infection: A simple cut or scrape can become infected if not properly cleaned and cared for. Infections can spread quickly, especially in deeper wounds, leading to cellulitis, sepsis, or even the loss of a limb.
- Internal Damage: A soft tissue injury or minor bruise could mask internal bleeding or organ damage. These issues may not be immediately visible but can worsen over hours or days.
- Undiagnosed Head Injuries: A bump on the head that causes mild dizziness might actually be a concussion or early-stage traumatic brain injury (TBI). Symptoms can intensify without proper monitoring and rest, and lead to long-term cognitive problems.
- Whiplash and Back Pain: Whiplash from a low-speed car accident may initially feel like soreness, but if not treated, it can result in chronic neck pain, limited mobility, and even nerve damage.
- Joint or Muscle Strains: A strained wrist or ankle might feel better after a few days, but hidden ligament tears or fractures can worsen with continued use, turning a minor strain into a severe injury that needs surgery.
- Delayed Symptoms: Some injuries don’t show immediate symptoms. You may feel fine after an accident, only to experience severe pain, swelling, or neurological issues days later. This delay is common in conditions like internal bleeding, disc herniation, or soft tissue injuries.
Signs That a Minor Injury May Be Getting Worse
- Increasing pain or swelling
- Numbness or tingling
- Loss of mobility or strength
- Redness, pus, or warmth at the site of injury
- Dizziness, fatigue, or confusion
- Symptoms lasting more than 1–2 weeks
What To Do If You’re Unsure
- Always consult a doctor after an accident, even if you feel okay.
- Document the injury and symptoms as they develop—this helps in both treatment and legal cases.
- Avoid self-treating serious pain with over-the-counter meds if symptoms persist or worsen.
Just because an injury looks or feels minor doesn’t mean it is. Minor injuries can quietly evolve into major health concerns if ignored. Taking the time to get a professional medical opinion can protect your long-term health, and if necessary, strengthen any insurance or legal claim you may need to make.

Legal Implications: Why the Distinction Between Major and Minor Injuries Matters
When it comes to personal injury law—especially in cases like car accidents, workplace incidents, or slip-and-fall injuries—the severity of the injury plays a major role in how a claim is handled, how much compensation is awarded, and how complex the legal process becomes.
1. Compensation Value
- Minor Injuries: Typically result in lower compensation because they involve limited medical costs, minimal recovery time, and little to no impact on long-term quality of life.
- Major Injuries: Often lead to substantially higher settlements or verdicts because they involve long-term medical care, loss of earning capacity, emotional distress, and sometimes permanent disability.
Example: A sprained ankle might result in a few hundred dollars in medical bills. But a spinal injury could lead to hundreds of thousands—or even millions—in compensation for surgery, rehab, and lifelong care.
2. Evidence Requirements
- Minor Injury Claims: Can usually be supported by basic medical documentation, such as a doctor’s note, prescription, or a single visit to an urgent care center.
- Major Injury Claims: Require detailed medical records, treatment plans, expert medical testimony, rehabilitation documentation, and sometimes psychological evaluations.
The more severe the injury, the more extensive and detailed the proof required to validate the damages.
3. Legal Complexity
- Minor Injury Cases: These are often resolved quickly through insurance claims or small settlements. These may not even require a lawyer in some jurisdictions.
- Major Injury Cases: Tend to be more complex and time-consuming, often involving disputes over liability, long-term projections, and negotiations or court trials. Skilled legal representation is strongly recommended.
4. Insurance Company Behavior
Insurers may readily settle minor injury cases to avoid unnecessary disputes. For major injuries, insurance companies may:
- Contest the severity of the injury
- Delay the claim
- Offer lowball settlements
- Push back on liability
In these cases, an experienced personal injury lawyer can negotiate, present strong evidence, and, if necessary, take the case to trial.
5. Statutory Thresholds & Lawsuits
In “no-fault” states like New York, victims typically must meet a “serious injury threshold” to sue outside of insurance. This includes:
- Fractures
- Permanent disfigurement
- Loss of limb or function
- Long-term disability
Minor injuries may not qualify for a personal injury lawsuit unless they escalate or meet certain legal criteria.
The legal system doesn’t just treat all injuries the same. The distinction between minor and major injuries directly affects:
- Whether you can sue
- How much can you recover
- How long does the process take
- How aggressively will the other side fight back
If you’ve suffered a major injury, it is critical to speak with a legal professional as early as possible to protect your rights and maximize your compensation.

When to Seek Medical Attention
After an accident or injury—no matter how minor it may seem—it’s always wise to get a medical evaluation. Many injuries don’t show symptoms immediately, and delaying treatment can lead to complications or worsen the condition.
Seek Medical Attention Immediately If You Experience:
- Severe pain or swelling
- Loss of movement or function in any body part
- Dizziness, confusion, or loss of consciousness
- Bleeding that won’t stop
- Signs of infection (redness, warmth, pus, or fever)
- Breathing difficulties or chest pain
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in limbs
Even if the injury appears mild, early diagnosis can prevent it from becoming more serious. Medical records from your visit also serve as important evidence if you plan to file an insurance or personal injury claim.

When to Call Emergency Services
Some injuries and symptoms are too serious to wait—calling emergency services (like 911 or 995) can be life-saving.
Call Emergency Services Immediately If Someone:
- Is unconscious or unresponsive
- Has trouble breathing or is gasping for air
- Is bleeding heavily and it won’t stop
- Has a suspected head, neck, or spinal injury
- Is having a seizure or chest pain
- Shows signs of a stroke (slurred speech, numbness, confusion)
- Has a serious burn, broken bone, or severe trauma
- Was shocked by electricity or severely injured in a car crash
In these situations, every second counts. Don’t hesitate—emergency professionals can provide life-saving care before the patient reaches the hospital.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between major and minor injuries isn’t just a matter of classification—it can directly impact your health, recovery, and legal rights. While minor injuries may heal with basic care and time, major injuries often require urgent treatment, long-term rehabilitation, and legal action to secure fair compensation.
Never assume an injury is too small to matter. Even seemingly minor symptoms can escalate into serious medical conditions if ignored. Seeking prompt medical attention, documenting your injury, and knowing when to call emergency services can significantly improve your recovery and your ability to protect your legal interests.
If you’ve suffered a serious injury due to someone else’s negligence—whether in a car accident, at work, or in a public space—don’t face the aftermath alone. Consult a medical professional for proper diagnosis and treatment, and speak with an experienced personal injury lawyer to explore your legal options.
Key Takeaways:
- Minor injuries are non-life-threatening and heal quickly.
- Major injuries require urgent care and can have lasting effects.
- What starts as a minor injury can worsen—never ignore symptoms.
- Early medical care protects both your health and legal rights.
- For serious injuries, consult a personal injury lawyer to explore your options.

