Manual handling is essential to many jobs but poses significant risks to workers. Whether lifting, carrying, pushing, or pulling objects, incorrect handling techniques can lead to serious injuries impacting the worker and the business.
In this blog post, we will explore the ten most common types of manual handling hazards and injuries that workers may encounter and give tips on how to avoid them. By understanding these hazards and taking necessary precautions, workers can reduce the risk of injury and stay safe while performing manual handling tasks.
What Is Manual Handling And Where Does It Occur?
Manual handling is a term used to describe the various physical activities that involve lifting, holding, putting down, pushing, pulling, carrying or moving an object or a load by one or more workers. This can include animate objects such as people or animals, or inanimate objects like boxes, tools, or equipment.
Manual handling activities can occur in almost all working environments such as factories, warehouses, construction sites, farms, hospitals, offices, and other workplaces. Workers in different industries or sectors may be exposed to varying degrees of manual handling risks.
According to the Fourth European Working Conditions Survey carried out in the EU-27 in 2005, approximately 35% of all workers are exposed to the risk of carrying or moving heavy loads for at least a quarter of their working time. This risk is especially high for skilled agriculture and fishery workers, craft and related trades workers, plant and machine operators, and assemblers. Young workers reportedly are the most exposed of all age groups.
Moreover, workers in certain industries or sectors are more likely to be exposed to heavy loads than others. For instance, workers in agriculture, construction, hotels, and restaurants have the highest exposure rates, with approximately 68%, 64%, and 48% respectively. Workers in the manufacturing and mining, wholesale and retail trade sectors have a slightly lower rate of exposure, around 42%, and those in the transport and communications industry have an exposure rate of 35%.
Manual handling can cause various musculoskeletal disorders such as sprains and strains, back injuries, and hernias, and can lead to long-term health problems if not managed properly. Therefore, it is important for employers to identify and manage manual handling risks, provide adequate training and equipment, and encourage safe work practices to prevent workplace injuries and improve the health and wellbeing of their employees.

Manual Handling Injuries and How To Avoid Them
Manual handling injuries occur due to lifting, carrying, pushing, or pulling heavy or awkward loads. These injuries can be serious, including sprains, strains, fractures, and permanent disability. Here are different types of manual handling injuries to avoid:
1. Strains And Sprain
Strains occur when muscles are overstretched or torn, while sprains occur when ligaments are stretched or torn. Both can result in pain, swelling, and reduced mobility.
Strains and sprains can occur during manual handling tasks that involve lifting, carrying, pushing, or pulling heavy objects or loads. These injuries can be acute or chronic. Acute strains and sprains occur suddenly and are usually caused by a single traumatic event, such as lifting a heavy object incorrectly or slipping and falling while carrying a load. On the other hand, chronic strains and sprains develop over time and are caused by repetitive motions or overuse of muscles and joints.
Preventing strains and sprains during manual handling involves:
- Assessing the load to ensure it is within your physical capabilities,
- Using proper lifting techniques such as bending your knees,
- Keeping your back straight, and
- Using appropriate equipment such as lifting aids or trolleys.
- It is also essential to take breaks and stretch before and after handling loads to avoid overuse and fatigue of muscles and joints.
2. Back Injuries
Back injuries are a common type of injury that can occur during manual handling tasks. Lifting heavy objects or loads can put a lot of stress on your back muscles and spine, leading to strains or sprains. Twisting or bending awkwardly while carrying a load can also strain your back muscles and increase the risk of injury.
Back injuries range from minor strains and sprains to more severe injuries such as herniated discs or fractures. Herniated discs occur when the soft cushioning material between the vertebrae in the spine ruptures or bulges out, putting pressure on nearby nerves and causing pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs or arms.
To prevent back injuries during manual handling tasks, it is important to:
- Use proper lifting techniques such as bending your knees,
- Keeping your back straight, and
- Using your leg muscles to lift the load instead of your back muscles.
It is also important to avoid twisting or bending awkwardly while carrying a load and to take regular breaks to rest your back muscles. Using appropriate lifting aids or trolleys can also help reduce the strain on your back. If you experience back pain or discomfort after a manual handling task, seeking medical attention and avoiding further lifting until you fully recover is important.
3. Hand And Wrist Injuries
Hand and wrist injuries are a common type of injury that can occur during manual handling tasks. Repetitive motions such as lifting, carrying, and grasping can strain your hand and wrist muscles, tendons, and ligaments, leading to injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome.
In addition to direct contact with the load, hand and wrist injuries can occur when placing the load down or maneuvering the load around obstacles. When placing a heavy load down, it is important to ensure that your fingers are clear of the load to avoid bruising or broken bones. During team lifts, it is important to communicate with other team members and ensure that everyone knows where their hands and fingers are in relation to the load.
To prevent hand and wrist injuries during manual handling tasks, it is important to:
- Use proper lifting techniques, such as gripping the load firmly and evenly,
- Using your whole hand and not just your fingers, and
- Avoiding over-gripping or under-gripping the load.
Appropriate gloves or hand protection can also help reduce the risk of cuts or burns from sharp or hot objects. It is also important to take regular breaks and stretch your hands and wrists to avoid overuse and fatigue of muscles and tendons. If you do experience hand or wrist pain or discomfort after a manual handling task, it is important to seek medical attention and avoid further lifting until you have fully recovered.

4. Neck Injuries
Neck injuries are another type of injury that can occur during manual handling tasks. Carrying loads that are too heavy or awkwardly shaped can strain your neck muscles, tendons, and ligaments, leading to strains and sprains.
When carrying a load, it is important to ensure it is evenly distributed and balanced on your shoulders or hands to avoid putting extra strain on your neck muscles. Carrying loads that are too heavy can also cause your neck to bend forward, leading to poor posture and an increased risk of injury.
To prevent neck injuries during manual handling tasks, it is important to:
- Assess the load to ensure it is within your physical capabilities and
- Use proper lifting techniques, such as keeping your back straight and your shoulders relaxed.
Using appropriate lifting aids or trolleys can also help reduce the strain on your neck muscles. Regular breaks and stretching of your neck muscles are also important to avoid overuse and fatigue. If you experience neck pain or discomfort after a manual handling task, seeking medical attention and avoiding further lifting until you fully recover is important.
5. Shoulder Injuries
Shoulder injuries are another common injury that can occur during manual handling tasks. Overhead lifting or carrying heavy loads on the shoulders can strain your shoulder muscles, tendons, and ligaments, leading to rotator cuff injuries and shoulder strains.
Rotator cuff injuries occur when the tendons or muscles in the shoulder are torn or damaged, leading to pain, weakness, and reduced mobility. Shoulder strains occur when the muscles and tendons in the shoulder are overstretched or torn, leading to pain and reduced mobility.
To prevent shoulder injuries during manual handling tasks, it is important to:
- Use proper lifting techniques, such as keeping your shoulders relaxed and
- Avoiding overhead lifting unless absolutely necessary.
Carrying loads on your shoulders should also be avoided unless the load is light and evenly distributed. Using appropriate lifting aids or trolleys can also help reduce the strain on your shoulder muscles. Regular breaks and stretching of your shoulder muscles are also important to avoid overuse and fatigue.
6. Crush Injuries
Crush injuries are a potential hazard that can occur during manual handling tasks involving heavy machinery or equipment. When handling heavy machinery or equipment, there is a risk of being crushed by the weight of the load or moving parts.
Crush injuries can occur when heavy objects are dropped or a person is trapped between the object and another surface, such as a wall or machinery. They can also occur when working around moving machinery with rotating parts or heavy equipment such as forklifts or cranes.
To prevent crush injuries during manual handling tasks, it is important to:
- Ensure that the equipment is in good working condition and
- Use appropriate lifting aids or equipment, such as forklifts or cranes, to move heavy loads.
When working around moving machinery, it is important to:
- Be aware of the hazards and follow all safety procedures, such as using guard rails
- Use lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental activation of machinery.
- It is also essential to wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as hard hats and safety shoes, to protect yourself from falling objects or debris.
- Finally, it is essential to receive adequate training and to work within your physical capabilities to reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.

7. Cuts And Lacerations
Cuts and lacerations are potential hazards during manual handling tasks involving sharp objects or materials. Handling sharp objects or materials can result in cuts or lacerations to the skin.
Cuts and lacerations can occur when handling sharp objects such as knives, scissors, or broken glass or when working with metal or wood with sharp edges or splinters. These injuries can range from minor cuts that require a simple first-aid treatment to more serious injuries that require medical attention.
To prevent cuts and lacerations during manual handling, it is important to:
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses, to protect yourself from sharp objects or materials.
- Handle sharp objects or materials carefully and avoid rushing or taking shortcuts that can increase the risk of injury.
When working with materials such as metal or wood, it is important to use appropriate tools and to inspect the material for sharp edges or splinters before handling. Finally, it is important to receive adequate training and to work within your physical capabilities to reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
8. Burns And Scalds
Burns and scalds are potential hazards when manually handling hot or caustic materials. Handling hot materials, such as hot liquids or hot surfaces, can result in burns, while handling caustic materials, such as acids or alkalis, can result in chemical burns.
Burns and scalds can range from minor burns requiring a simple first-aid treatment to more serious ones requiring medical attention. Chemical burns can also cause damage to the skin and eyes and require immediate medical attention.
To prevent burns and scalds during manual handling, it is important to:
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment, such as heat-resistant gloves and aprons to protect yourself from hot or caustic materials.
- Handle hot or caustic materials carefully and avoid rushing or taking shortcuts that can increase the risk of injury.
When working with hot materials such as hot liquids, it is important to use appropriate containers and to allow the material to cool before handling. When working with caustic materials, following appropriate safety procedures, using appropriate containers, and handling equipment is important. Finally, it is important to receive adequate training and to work within your physical capabilities to reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
9. Hernias
Hernias are a potential hazard that can occur during manual handling tasks. A hernia occurs when an internal part of the body pushes through a weakness in the muscle or surrounding tissue wall, often in the abdomen or groin area.
Repeated strain on the abdominal muscles from manual handling tasks such as lifting or carrying heavy loads can increase the risk of developing a hernia. Age can also be a factor, as the abdominal muscles weaken over time.
To prevent hernias during manual handling tasks, assessing the load and the individual’s physical capabilities is important to:
- Ensure that the load is within its safe lifting capacity.
- Using appropriate lifting aids or equipment, such as trolleys or hoists can also help reduce the strain on the abdominal muscles.
- Avoid over-straining and use proper lifting techniques such as bending the knees and keeping the back straight.
Taking regular breaks and avoiding overuse and fatigue can also help reduce the risk of developing a hernia. Finally, it is important to seek medical attention if you experience any hernia symptoms, such as pain or a bulge in the abdominal or groin area.
10. Foot And Ankle Injuries
Foot and ankle injuries are other potential hazards during manual handling tasks. Carrying heavy loads can put a lot of strain on your feet and ankles, leading to sprains and strains.
In addition to sprains and strains, dropping a heavy load on your foot or being struck by a falling object can result in fractures or other serious injuries to the foot and ankle. Wearing inappropriate or inadequate footwear can also increase the risk of foot and ankle injuries during manual handling tasks.
To prevent foot and ankle injuries during manual handling tasks, it is important to:
- Wear appropriate footwear, such as safety shoes or boots with slip-resistant soles to protect your feet and improve traction.
- Use proper lifting techniques, such as keeping your back straight and your feet shoulder-width apart. Appropriate lifting aids or trolleys can also help reduce the strain on your feet and ankles.
- Take regular breaks and stretch your feet and ankles to avoid overuse and fatigue of muscles and tendons.
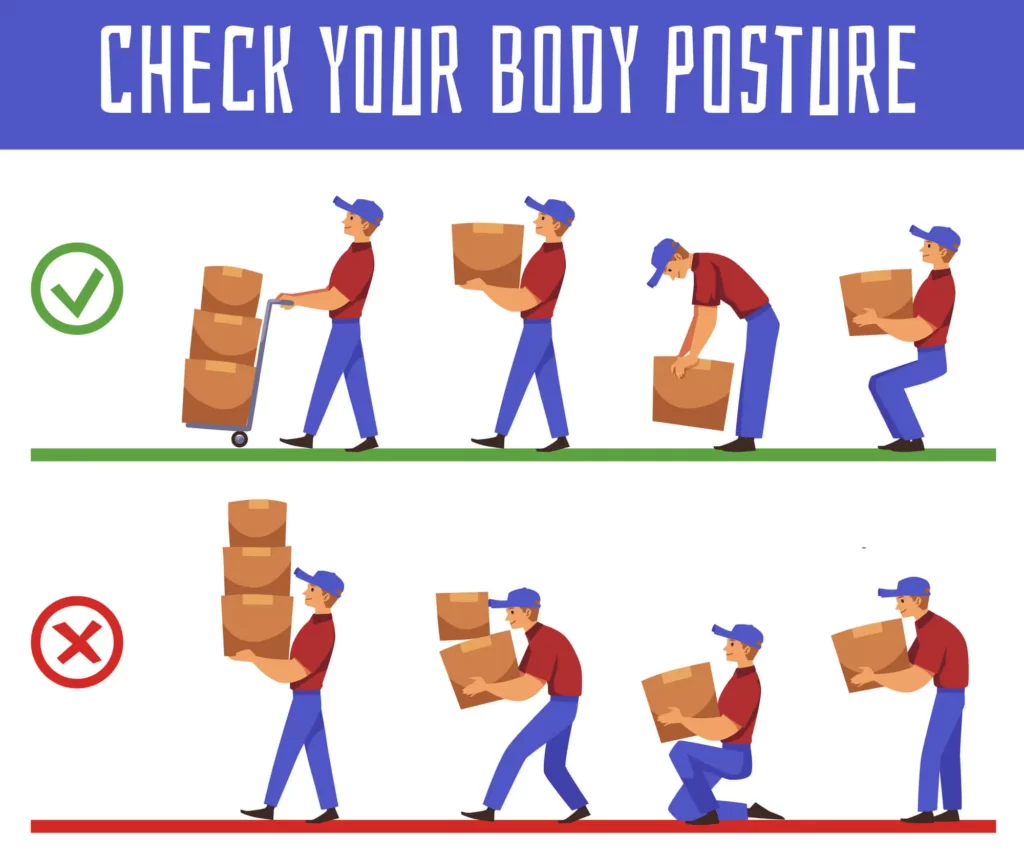
Manual Handling Hazards and How To Avoid Them
Manual handling is lifting, carrying, pushing, or pulling loads manually. It is a common cause of work-related injuries, including strains, sprains, and musculoskeletal disorders. Here are some common manual handling hazards and how to avoid them:
1. Heavy Loads
Heavy loads can pose a significant hazard to workers required to lift or carry them. Lifting or carrying heavy objects can cause a strain on the muscles, particularly in the back and legs, which can lead to serious injuries. Some common tasks involving heavy loads include lifting boxes, carrying equipment, and loading or unloading trucks.
Heavy loads can be hazardous because they require significant physical effort and, if not handled correctly, can cause injury. Lifting heavy loads can cause lower back pain, hernias, and other musculoskeletal disorders, leading to long-term health problems if left untreated.
To prevent injuries related to heavy loads, it is important for employer to:
- Identify tasks involving heavy loads and develop strategies to minimize their weight and the lifting frequency.
- Provide lifting aids, such as hand trucks, pallet jacks, or forklifts, to help workers move heavy loads safely.
2. Repetitive Motions
Repetitive motions can cause muscle fatigue and strain, leading to injury. This is because the same muscles are used repeatedly without sufficient time to rest and recover, which can cause micro-injuries that accumulate over time. Some common tasks involving repetitive motions include lifting and moving boxes, packing products, and sorting items.
Repetitive motion injuries can manifest in various forms, including tendonitis, bursitis, carpal tunnel syndrome, and other musculoskeletal disorders. These injuries can cause pain, swelling, stiffness, weakness, and numbness in the affected area, leading to chronic conditions if left untreated.
To prevent repetitive motion injuries, it is important for employer to:
- Identify tasks that involve repetitive motions and develop strategies to reduce their frequency or duration.
- Introduce job rotation or task-sharing schemes, providing rest breaks or job redesign to incorporate activities allowing rest periods for the muscles involved.
3. Awkward Postures
Working in awkward postures, such as bending, twisting, or reaching overhead, can strain the back and other body parts. These postures can lead to musculoskeletal disorders, such as back, neck, and shoulder pain, if sustained for long periods or performed frequently.
Awkward postures can be caused by various factors, including inadequate workspace design, the need to reach or stretch to access objects, and improper body mechanics. Some common tasks involving awkward postures include packing products, working on assembly lines, and installing equipment.
To prevent injuries related to awkward postures, it is important for employer to:
- Identify tasks involving them and develop strategies to minimize their frequency and duration.
- Conduct ergonomic assessments to identify and address potential workspace design and equipment layout issues.
- Make adjustments to improve the posture and reduce the strain on the worker’s body.

4. Unstable Loads
Unstable loads can pose a significant hazard to workers required to carry or transport them. Unstable loads are not evenly distributed, balanced, or secured, which can cause the worker to lose their balance and fall. Some common tasks involving unstable loads include carrying buckets of liquid, transporting items on a cart, and moving unbalanced equipment.
Unstable loads can be hazardous because they require the worker to maintain their balance while carrying or transporting the load, which can be difficult if the load is unstable or unbalanced. This can cause workers to lose their balance and fall, resulting in serious injury.
To prevent injuries related to unstable loads, it is important for employer to:
- Identify tasks involving them and develop strategies to minimize the risk of falls.
- Provide equipment, such as carts with stable bases, to help workers transport unstable loads safely.
5. Insufficient Space
Working in cramped or confined spaces can pose a significant hazard to workers required to move or maneuver loads within those spaces. Insufficient space can make it difficult for workers to move freely, which can cause them to hit or bump into objects or to be struck by falling objects. Some common tasks involving insufficient space include loading or unloading trucks, working in storage rooms or closets, and installing equipment in tight spaces.
Insufficient space can be hazardous because it requires workers to maneuver loads within limited spaces, increasing the risk of injury. This can cause the worker to strain their muscles, particularly in the back and arms, or to be struck by the load or other objects.
To prevent injuries related to insufficient space, it is important for employer to:
- Identify tasks that involve working in cramped or confined spaces and develop strategies to minimize the risk of injury.
- Provide equipment, such as carts with small turning radii, to help workers move and maneuver loads safely within limited spaces.
6. Poor Grip
Poor grip or slipperiness of objects can pose a significant hazard to workers required to handle those objects. A poor grip can make it difficult for workers to maintain their grip on the load, which can cause it to slip or fall, potentially resulting in injury. Some common tasks involving poor grip include handling wet or oily surfaces, transporting items with smooth surfaces, and carrying loads with uneven or jagged edges.
A poor grip can be hazardous because it requires workers to exert more force to maintain their grip on the load, increasing the risk of injury. This can cause the worker to strain their muscles, particularly in the hands and arms, or to be struck by the load or other objects.
To prevent injuries related to poor grip, it is important for employer to:
- Identify tasks that involve handling objects with poor grip and develop strategies to minimize the risk of injury.
- Provide equipment, such as gloves with non-slip surfaces, to help workers maintain their grip on the load.

7. Poor Lighting
Poor lighting conditions can pose a significant hazard to workers required to perform tasks in those conditions. Poor lighting can make it difficult for workers to see potential hazards, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries. Some common examples of tasks that involve poor lighting include working in storage areas or rooms with inadequate lighting, performing tasks outdoors during low-light conditions, and working in areas with limited natural light.
Poor lighting can be hazardous because it can obscure potential hazards, such as uneven surfaces or obstacles, increasing the risk of slips, trips, and falls. It can also make it difficult for workers to identify potential hazards, such as dangerous machinery or sharp objects, increasing the risk of injury.
To prevent injuries related to poor lighting, it is important for employer to:
- Identify tasks that involve working in poor lighting conditions and develop strategies to improve lighting.
- Install additional light sources, such as lamps or overhead lights, to increase the amount of available light.
- Install reflective surfaces like mirrors or white walls to reflect available light and improve visibility.
Conclusion
Manual handling hazards are common in many workplaces, and it is crucial to identify and control them to prevent injuries and accidents. Workers should be trained in safe manual handling techniques and provided with appropriate tools and equipment to reduce the risk of harm. Employers have a legal obligation to assess manual handling tasks and put in place measures to minimize risks to their workers.
By taking steps to address manual handling hazards, employers can improve the health and safety of their employees and create a safer working environment. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, so it is essential to take proactive steps to avoid manual handling injuries in the workplace.

