Diving into the intriguing world of chemical compounds, today we shift our focus to a potent and versatile substance – Glutaraldehyde. This powerful disinfectant might not be a common topic at the dinner table, but its presence and influence span numerous sectors, from healthcare to cosmetics and industrial applications.
This comprehensive guide will demystify Glutaraldehyde, exploring its uses, the potential health effects of exposure, and the key safety measures for handling and storage. It’s crucial information for professionals interacting with this compound regularly and equally intriguing for anyone keen on expanding their scientific knowledge.
What is Glutaraldehyde?
Glutaraldehyde is an organic compound used as a disinfectant, preservative, and sterilant. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor found in various forms, including powder, pellets, or solution. Glutaraldehyde is mostly used in hospitals and other medical settings to sterilize surgical instruments and equipment due to its potent antimicrobial properties. It has also been used in cosmetics and consumer products as a preservative and to prevent microbial growth. Glutaraldehyde is toxic and can cause skin, eye, and respiratory irritations, so it should be handled cautiously.
Glutaraldehyde Uses
Glutaraldehyde has many uses, primarily due to its strong disinfecting and sterilizing properties. Here are some of the main uses of this compound:
- Medical Applications: Glutaraldehyde is commonly used in hospitals and other healthcare settings to sterilize surgical and medical equipment. It can kill many microorganisms, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi. It is used in solutions for cold sterilization of heat-sensitive equipment.
- Histology and Microscopy: In biology, glutaraldehyde is a fixative for microscopy and histology. It helps to preserve the structure of cells and tissues for examination under a microscope.
- Industrial Applications: In the oil and gas industry, glutaraldehyde is used as a biocide in water treatment systems to control microbial growth. It’s also used in the leather tanning process for its cross-linking properties.
- Dental Industry: In dentistry, glutaraldehyde is a disinfectant and cavity disinfectant. It’s also used in impression materials.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care Products: It can also be found in some cosmetics and personal care products as a preservative to prevent microbial growth.
- Electron Microscopy: Glutaraldehyde is used to fix biological tissues for electron microscopy.
Although glutaraldehyde is effective for these uses, it’s a potent chemical that can cause harm if not handled properly. Always follow safety guidelines when using this compound.
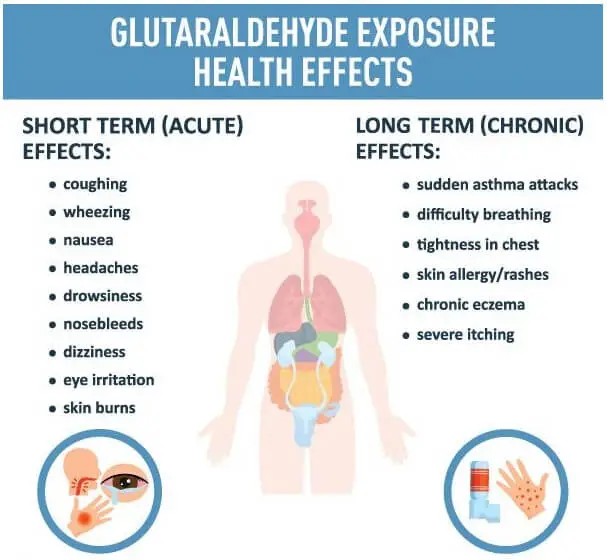
Effects Of Glutaraldehyde Exposure
Exposure to glutaraldehyde, especially in high concentrations or over long periods of time, can have various health effects.
- Skin and Eye Irritation: Glutaraldehyde can cause skin irritation, leading to redness, pain, and burns. It can also cause serious eye irritation or damage. Even small amounts can cause severe burns and eye damage, leading to conditions such as conjunctivitis or blindness.
- Respiratory Effects: Inhalation of glutaraldehyde fumes can lead to respiratory tract irritation. This can cause symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. It can lead to chemical pneumonitis and pulmonary edema, serious and potentially life-threatening conditions in severe cases.
- Sensitization: Some individuals can become sensitized to glutaraldehyde. This means they can develop an allergic reaction to the compound, leading to skin rashes, itching, and respiratory symptoms upon future exposure. Sensitization can occur even at very low exposure levels.
- Neurological Effects: High-level or long-term exposure to glutaraldehyde can lead to neurological symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and in severe cases, it may cause unconsciousness.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: If ingested, glutaraldehyde can cause nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- Chronic Effects: Chronic exposure to glutaraldehyde can result in persistent respiratory symptoms and can also lead to chronic skin problems such as dermatitis.
Given these potential health hazards, it is crucial to handle glutaraldehyde with care and to use appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and eye protection, when handling this substance. Always use it in a well-ventilated area or under a chemical fume hood, and avoid skin and eye contact and inhalation of the vapors. In case of exposure, seek immediate medical attention.

The Handling and Storage Of Glutaraldehyde
The handling and storage of glutaraldehyde require careful attention due to its toxic and irritating properties. Here are some key guidelines:
Handling Glutaraldehyde:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE when handling glutaraldehyde. This may include gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats. In some cases, respiratory protection may also be required.
- Ventilation: Glutaraldehyde should be used in a well-ventilated area to prevent inhalation of the fumes. If possible, use it under a fume hood.
- Safe Practices: Avoid direct skin and eye contact. Don’t ingest it, and avoid breathing in its vapors or mists.
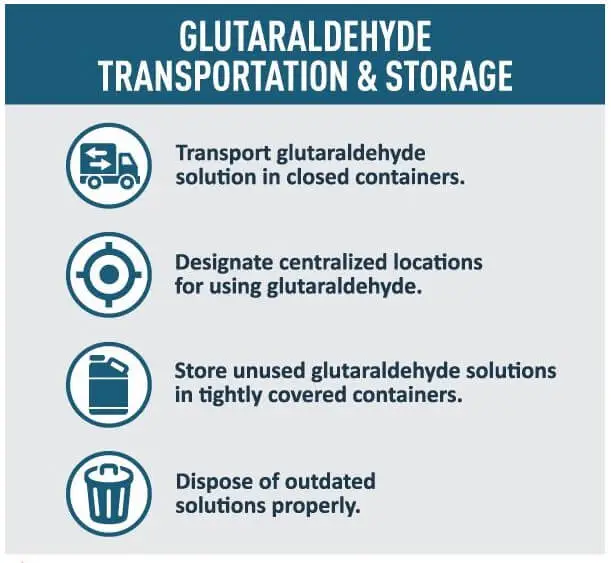
- Waste Disposal: Dispose of glutaraldehyde waste according to local regulations. Don’t pour it down the drain.
Storing Glutaraldehyde:
- Proper Container: Store glutaraldehyde in a tightly sealed container to prevent leakage and evaporation.
- Proper Location: Store it in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from heat sources and direct sunlight.
- Avoid Mixing: Keep it separate from incompatible substances such as strong oxidizing agents, acids, bases, and metals.
- Proper Labeling: The storage container should be clearly labeled with the name of the substance, hazard symbols, and safety information.
- Safety Data Sheets: Keep Safety Data Sheets (SDS) accessible where glutaraldehyde is stored. The SDS provides detailed information about the substance, including its hazards, safety precautions, and first aid measures.
- Spill and Emergency Procedures: Have procedures for handling spills and other glutaraldehyde emergencies. This includes having appropriate spill-cleanup materials available.
Overall, the key to safely handling and storing glutaraldehyde is to follow proper safety protocols, use appropriate protective equipment, and be aware of the potential hazards associated with this substance. Always handle glutaraldehyde with care to minimize the risk of exposure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, glutaraldehyde is a powerful disinfectant and sterilant that serves critical roles across multiple sectors, from healthcare to industry and even cosmetics. Its ability to eradicate many microorganisms makes it an indispensable tool, particularly in medical environments. However, it’s not without its risks – exposure can lead to various health effects, including respiratory issues, skin irritation, and more. Therefore, strict adherence to safety protocols is necessary when handling and storing this chemical. By understanding what glutaraldehyde is, its uses, the potential effects of exposure, and the correct handling and storage procedures, we can utilize this potent compound responsibly and safely, harnessing its benefits while mitigating its potential hazards.

