In the fast-paced industrial world, machinery is the lifeblood that keeps production lines humming and the gears of progress turning. However, this essential machinery can pose a significant hazard to the workforce if not managed meticulously. A critical aspect of ensuring the safety and efficiency of an industrial environment is the strategic placement of machinery and the establishment of safe working distances around it.
This insightful article will explore the crucial interplay between where machinery is positioned within a facility and how much space is maintained around it to safeguard workers. Whether you are a business owner, a safety manager, or an employee in the manufacturing, construction, or any industry with heavy machinery, this article is geared to enlighten you on best practices for creating a safe and productive workspace. Let’s set the wheels in motion!
Machine Location: Why It’s Important?
Machine location is integral to ensuring safety and productivity in an industrial setting. The positioning of machinery within a workspace can directly impact the efficiency of operations and the safety of employees. Here are some key reasons why machine location is critically important:
Safety of Employees
As a priority, machine location must be configured to minimize worker risks. Machinery, particularly in manufacturing and construction environments, can be hazardous. Placing machinery strategically can prevent accidents like entanglement, cuts, or crushing injuries by keeping dangerous moving parts away from areas where workers are present.
Workflow Efficiency
An efficient workflow is essential for productivity. By placing machines in locations that align with the production process, you can reduce the movement of materials and staff, thus lowering the time a product takes to move through the assembly line. This can directly impact the profitability and competitiveness of a business.

Ease of Maintenance
Machines require regular maintenance. Placing machinery where it is accessible for maintenance can reduce downtime and ensure that it operates efficiently and safely. On the contrary, poorly positioned machines may hinder maintenance activities, making them more time-consuming and costly.
Optimal Space Utilization
Space is a limited resource in most industrial settings. Proper machine location can help make the most out of the available space. By strategically positioning machines, you can ensure enough space for workers to move around safely and enough room for storage and other functions.
Energy Efficiency
The location of machinery can also affect energy consumption. For example, positioning machines closer to power sources can reduce the length of cabling required and lower energy losses. Moreover, positioning heat-generating machinery in areas with better ventilation can reduce cooling costs in a temperature-controlled environment.
Noise and Vibration Reduction
Machinery often generates noise and vibrations. By placing machines in specific locations, especially away from areas where employees spend most of their time, you can reduce exposure to potentially harmful noise levels and vibrations. Additionally, the proper location can prevent the transfer of vibrations to other equipment, which could affect their performance or lifespan.
Flexibility for Future Expansion
Businesses need to evolve and adapt. When planning the location of machinery, considering potential future expansions or alterations is vital. This allows for greater flexibility when adding new equipment or reconfiguring production lines.
Compliance with Regulations
Regulatory bodies often have specific requirements regarding the placement of machinery, especially regarding safety. Proper machine location is necessary to comply with these regulations and avoid fines or legal issues.
Machine Location And Safe Working Distances Around Machinery
When installing and operating machinery in a workspace, it is crucial to consider both the location of the machine and the safe working distances around it. These considerations ensure the safety and efficiency of operations. Here is a guide to help establish a safe working environment around machinery:
- Assess the Workspace: Before installing machinery, evaluate the workspace to ensure there is enough space for the machine, personnel, and for material handling equipment.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Check the manufacturer’s instructions for any specific requirements regarding space around the machine. The guidelines usually include information on the minimum safe distances to be maintained.
- Consider the Operational Space: The space around the machinery should be adequate for its operational needs. This includes space for moving parts, materials, and products entering and exiting the machine.
- Allow Room for Maintenance and Inspection: Ensure enough space around the machine for routine maintenance and inspection. This will make it easier for personnel to perform these tasks safely and efficiently.
- Account for Clearance: There should be clear paths for moving materials, products, and personnel. This is important for preventing accidents and ensuring efficient workflow.
- Safety Zones and Barriers: Establish safety zones around machines with moving or hot parts to prevent accidental contact. Safety barriers, guard rails, or marking on the floor can be used to define these zones.
- Emergency Exits: Ensure that the location of the machinery does not block or hinder access to emergency exits. It’s vital that personnel can quickly and safely evacuate in case of an emergency.
- Ergonomics: Position machinery to minimize stress on workers’ bodies. This includes considering the height and reach of machine controls and the movement of personnel around the machine.
- Ventilation and Noise Levels: Position machines in a way that considers the ventilation needs of the machine and minimizes noise exposure to workers. This may require additional consideration for machines that produce fumes, dust, or high noise levels.
- Lighting: Ensure adequate lighting around the machinery for safe operation. The location should not cause shadows or glare hindering the operator’s visibility.
- Training and Signage: Train personnel on safe operating distances and the hazards associated with the machinery. Clear signage should be in place to remind workers of these distances and potential hazards.
- Adhere to Regulations and Standards: Comply with local, national, and international regulations and standards regarding machinery installation and safe working distances. This includes OSHA guidelines in the United States and similar bodies in other countries.
Remember that machine location and safe working distances are not static and may need to be reassessed as operations change, new equipment is added, or regulations evolve. Regularly review and update your safety procedures to maintain a safe working environment.
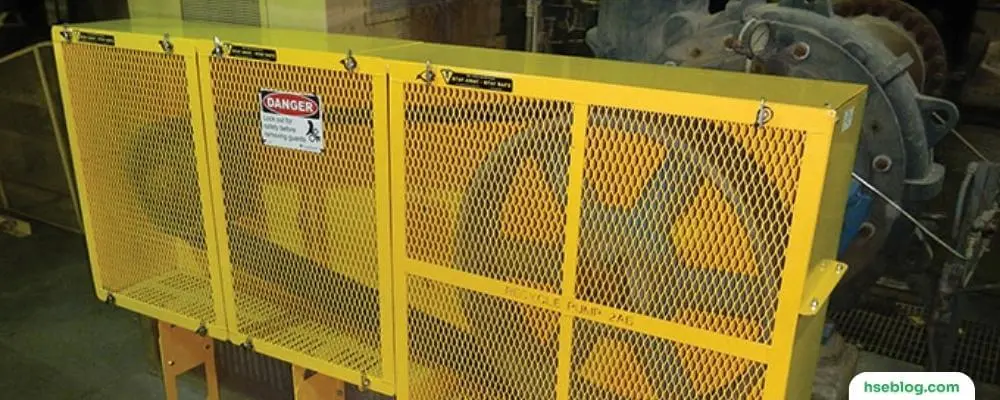

Concept of Machine Safeguarding by Location
Machine safeguarding by location is a critical component of workplace safety protocols. It focuses on strategically positioning machinery to mitigate the risks of employees coming into contact with hazardous parts. Understanding and effectively implementing this concept is key to reducing accidents and ensuring a safe work environment. Here, we delve deeper into the two primary aspects of machine safeguarding by location:
1. Location Away from Workstations
What Does it Entail?
Positioning machinery away from workstations involves thoughtful planning and layout of the workspace. This means situating machinery so that the hazardous components, especially the moving parts, are not near areas where employees frequently walk or work.
Why is it Important?
Separating workstations from machines with hazardous components significantly reduces the likelihood of accidental contact. Workers can go about their daily tasks without worrying about coming too close to machinery that could cause injury. This also results in fewer distractions, which can lead to increased productivity.
Implementation
Several factors should be considered in implementing this aspect of safeguarding by location:
- Workspace Layout Planning: Before installing machinery, it is important to have a well-thought-out plan considering the flow of employees, materials, and work processes. Avoid placing machinery with hazardous parts near high-traffic areas.
- Buffer Zones: Creating buffer zones around machinery can be an effective way to ensure there is sufficient distance between the machinery and workstations. This can be done using physical barriers or markings on the floor.
- Reorganization and Retrofitting: In cases where machinery is already installed, it might be necessary to reorganize the workspace or retrofit machines to make them safer.
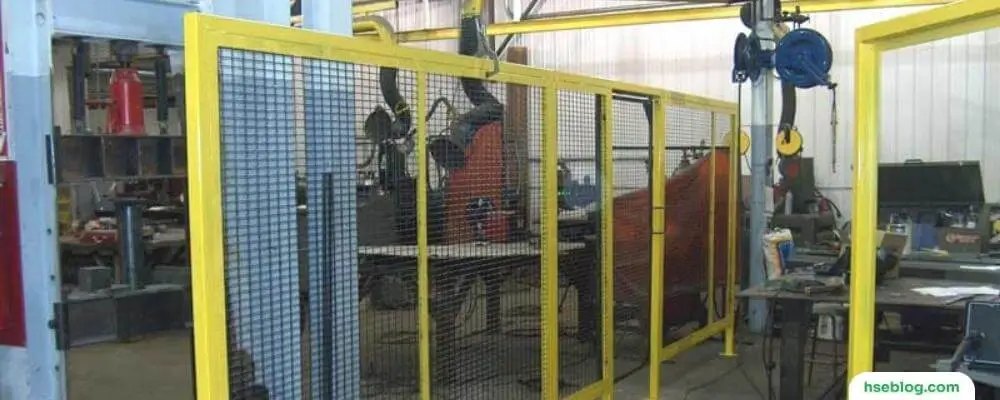

2. Power Transmission Apparatus Against a Wall
What Does it Entail?
This involves positioning machinery so that its power transmission apparatus (the components that transmit energy to the parts that perform the work, such as belts, gears, and motors) is against a wall. All routine operations and employee traffic should be on the opposite side, creating a physical barrier preventing access to these dangerous parts.
Why is it Important?
The power transmission apparatus of a machine is often one of the most dangerous parts because it is where energy is being transferred at high speeds. By positioning this part of the machine against a wall, you eliminate the possibility of someone accidentally coming into contact with it.
Implementation
- Machine Orientation: When setting up machinery, ensure the power transmission apparatus faces the wall. This might require custom installations or alterations to the machine layout.
- Physical Barriers: In addition to using the wall as a barrier, it can be beneficial to add extra physical barriers, such as fencing or plexiglass, to further secure the area around the power transmission apparatus.
- Maintenance Protocols: Ensure that maintenance protocols include safety measures for when someone must access the power transmission apparatus side of the machine. This might include lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the machine is not powered during maintenance.
Conclusion
In summary, the deliberate and strategic placement of machinery and maintaining safe working distances are imperative for fostering a safe and efficient workplace. By focusing on aspects such as employee safety, workflow efficiency, maintenance accessibility, and compliance with regulations, organizations can create an environment where productivity thrives without compromising the workforce’s well-being. It’s essential to remain vigilant and adaptive, continuously reassessing and optimizing machine locations and safe working distances to suit evolving needs and standards.

