In the intricate world of industrial machinery and safety systems, the principle of simplicity often shines brightest. Among the myriad of complex devices designed to keep our operations safe, the fusible plug stands out as an emblem of simplicity and effectiveness. But what exactly is a fusible plug, and why has it become such a revered component in various industries?
Dive into this comprehensive guide as we unravel the essence of fusible plugs and delve into the top 10 safety benefits they offer, underlining their indispensable role in ensuring operational safety and efficiency. Whether you’re a seasoned engineer or just curious about industrial safety mechanisms, this exploration promises to shed light on a device that quietly, yet confidently, guards against potential hazards.
What is a Fusible Plug?
A fusible plug is a specialized safety device, prominently used across various applications such as compressed air systems, steam systems, well heads, and especially in coal-fired boilers. Its inception and widespread usage can be attributed to its primary role as a preventive measure against hazardous situations. It acts as an advanced warning system, ensuring that machinery and systems don’t succumb to damages, or worse, explode due to soaring temperatures that surpass operational limits.

Structure and Composition
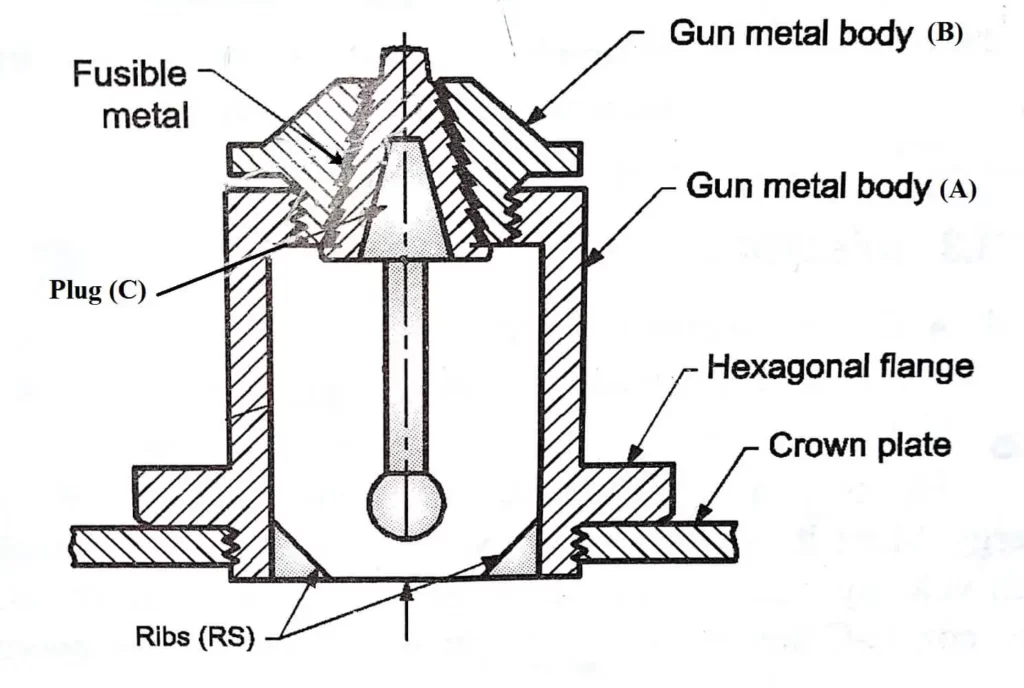
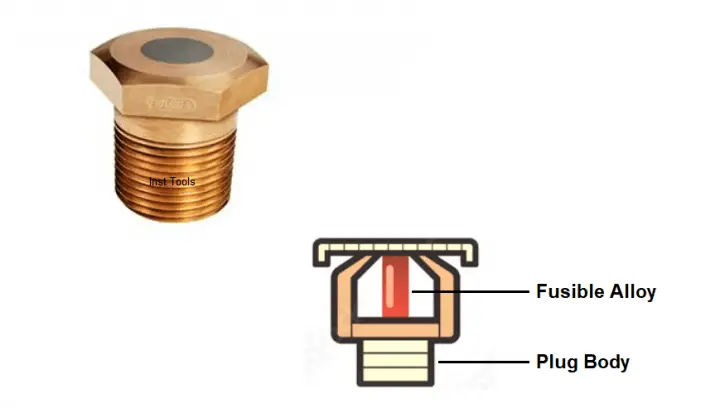
Delving into its anatomy, a fusible plug is meticulously crafted. The outer structure, which is the threaded body, is often fashioned from metals like brass, bronze, or gunmetal. These metals are chosen for their durability and resistance to high temperatures. However, the heart of this device is the fusible alloy encased within this metallic body.
The fusible alloy is not just any random metal; it’s selected based on its ability to melt at a temperature significantly lower than the plug’s outer body. Tin stands out as a preferred choice for this purpose, primarily because of its melting threshold, which is pegged at 232°C (450°F).
How Does Fusible Plug Work?
The fusible plug’s operational mechanics revolve around the fusible alloy’s melting prowess. When the environment or the machinery where the plug is installed experiences temperatures that exceed the alloy’s melting point, the alloy undergoes a phase change, transforming from solid to liquid. This melting action is not just a passive occurrence; it paves the way for a deliberate and strategic venting mechanism. As the alloy melts, it leaves behind a channel within the plug. This void now becomes a conduit, facilitating the escape of any pent-up system pressure.
The destination for this vented pressure varies based on the plug’s installation site. In compressed air systems scenarios, the vented pressure typically finds solace in the immediate surroundings. However, in the confines of boilers, particularly those powered by coal, the vented pressure is channeled into sections like the furnace or firebox.
Adding to the sophistication of its design, the fusible plug isn’t just about silent operation. As the pressure makes its egress, the plug is often constructed to produce a characteristic whistling sound. This isn’t just a byproduct of its design but a calculated feature. This auditory cue serves as a critical alert mechanism, immediately drawing operators’ attention to the fact that the machinery or system is undergoing an abnormal spike in temperature.
Why Use a Fusible Plug?
At its core, the fusible plug is the embodiment of simplicity paired with high efficiency. It’s not laden with complex circuits or intricate parts, yet its contribution to safety is monumental. By being a harbinger of potential temperature anomalies and offering an avenue for pressure relief, it staunchly defends machinery and systems from the perils of excessive heat. Its relevance is most pronounced in coal-fired boilers, but that’s not to say it’s limited to just that domain.
While boilers that run on alternatives like light fuel oil or gas might sometimes forgo the inclusion of a fusible plug, its importance cannot be understated. In various industrial terrains, it remains a sentinel, shielding machinery and human operators from the risks associated with temperature-induced mishaps.
10 Safety Benefits Of Using Fusible Plugs
Fusible plugs are safety devices commonly used in industrial applications to prevent catastrophic failures and accidents, especially in environments with high pressures and temperatures. These plugs are designed to melt or rupture when conditions are met, releasing pressure or performing a specific safety function. Here are some safety benefits of using fusible plugs:
1. Early Warning System
A fusible plug’s primary function is to act as a guardian against escalating temperatures. When temperatures surpass a safe threshold, the fusible alloy inside the plug melts, immediately releasing the built-up pressure.
For operators, this instantaneous response is invaluable. It indicates that the system is entering a potentially dangerous state. This real-time alert gives operators a crucial window to initiate corrective actions, averting more severe consequences and enabling a proactive approach to system management.
2. Prevention of Explosions
Equipment and machinery that deal with high pressures or temperatures are inherently at risk of explosions if safety mechanisms fail. As pressure-release valves, fusible plugs become the frontline defense against such threats.
By allowing a controlled venting of excessive pressure, they ensure that machinery never reaches the critical pressure points where explosions are possible. This safeguard is pivotal for preserving equipment and is a lifesaver for operators and nearby personnel.
3. Simple Design, Reliable Operation
Complexity often brings a higher chance of malfunction due to multiple components. The beauty of fusible plugs lies in their elegant simplicity. With fewer moving parts or intricate electronics, the possibility of a malfunction diminishes significantly. This unassuming design ensures that the fusible plug performs consistently when faced with a critical situation, delivering the safety promise it’s designed for.
4. Economic Safety Measure
In the industrial world, safety often comes with a hefty price tag. However, fusible plugs defy this norm. Their construction, while effective, is not expensive. This cost-effectiveness ensures that even tight-budget operations can afford this critical safety mechanism. Businesses don’t have to choose between safety and affordability, as fusible plugs deliver both.
5. Audible Alert Mechanism
Beyond the physical pressure venting, many fusible plugs have an added auditory feature. When activated, they produce a distinctive whistling sound, acting as an alarm. This audible alert ensures that even if an operator misses visual cues of a problem, the sound will immediately draw attention to the issue. In noisy industrial settings, such clear auditory warnings can be the difference between timely intervention and mishap.

6. Minimized Fire Risk
Especially in coal-fired boilers, where combustible materials are ever-present, the risk of fires due to trapped overheated steam or air is a significant concern. Fusible plugs, by enabling the swift release of such overheated substances, drastically reduce the chances of spontaneous fires, thereby ensuring the safety of the machinery and the surrounding environment.
7. Reduced Equipment Damage
Machines exposed to prolonged high temperatures or excessive pressure undergo stress, leading to faster wear and tear or irreversible damage. Fusible plugs ensure that machinery remains within operational limits by venting out excessive pressure. This not only extends the lifespan of the equipment but also translates to cost savings in the long run due to reduced maintenance and replacement expenses.
8. Versatility across Systems
The adaptable nature of fusible plugs makes them suitable for diverse systems. Whether a compressed air system in a manufacturing plant or a steam boiler in an energy facility, the fusible plug can be seamlessly integrated, providing consistent safety benefits irrespective of the operational environment.
9. Facilitates Emergency Protocols
Safety in industrial settings often requires a multi-tiered approach. The activation of a fusible plug can be a trigger for a cascade of other safety protocols. It can be synced with other systems so that when it vents, automated emergency procedures, from shutting down sections of a facility to alerting central control rooms, can be initiated, ensuring a comprehensive response to potential threats.
10. Boosts Operator Confidence
At the heart of any operation are its people. Knowing that robust safety mechanisms like fusible plugs are in place is a morale booster for operators. This confidence improves productivity, as operators can focus on their tasks without worrying about potential dangers. In the long run, such peace of mind contributes to a healthier work environment and improved operational efficiency.
Advantages and Disadvantages Of Using Fusible Plug
Advantages of Using Fusible Plugs:
- Simple and Reliable: With few components, fusible plugs have a straightforward design that ensures consistent performance when faced with a critical situation.
- Cost-Effective: Fusible plugs are relatively inexpensive compared to other safety devices, making them an affordable safety measure for many systems.
- Early Warning System: The melting of the fusible alloy offers a real-time alert, signaling operators to initiate corrective actions before situations escalate.
- Prevents Overpressure Explosions: Fusible plugs reduce the risk of catastrophic explosions by venting excessive pressure when temperature thresholds are exceeded.
- Audible Alert Mechanism: Many fusible plugs emit a distinct whistling sound when activated, offering an immediate auditory warning.
- Versatile: Fusible plugs can be integrated into various systems, from boilers to compressed air systems, ensuring consistent safety across multiple platforms.
Disadvantages of Using Fusible Plugs:
- One-Time Use: Once a fusible plug activates, it can’t be reused. It must be replaced after the alloy has melted, which can mean repair downtime.
- Potential for Inaccurate Activation: Over time, the fusible alloy can degrade or become contaminated, leading to premature melting or failure to melt at the correct temperature.
- Not Suitable for All Applications: While fusible plugs are versatile, they aren’t appropriate for every type of system or machinery, especially where precise temperature control is required.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Periodic checks are necessary to ensure the fusible alloy is in good condition and hasn’t corroded or been compromised.
- Delayed Response in Some Conditions: Under certain conditions, especially if there’s an external cooling source, the fusible alloy might not melt quickly enough to prevent damage or injury.
- Dependent on Correct Installation: The effectiveness of a fusible plug depends on its correct installation. If installed improperly, it may not provide the intended protection.
Conclusion
The industrial landscape is replete with intricate devices and systems, yet it’s often the most unassuming ones that leave an indelible mark. With its simple design, the fusible plug serves as a testament to this notion. Acting as both a guardian and a herald, it not only prevents potential catastrophes but also signals operators at the first sign of trouble. As we’ve journeyed through its numerous safety benefits, it becomes evident that the fusible plug is more than just a component; it’s a silent sentinel that prioritizes safety above all.
In an era where technology continually evolves, the enduring relevance of the fusible plug reminds us that, sometimes, simplicity paired with purpose can offer the most robust solutions. Whether safeguarding machinery or protecting human lives, the fusible plug’s contributions to industrial safety are unparalleled and undeniable.

