Understanding the intricacies of Mobile Elevating Work Platforms (MEWPs) is crucial for anyone working in industries where working at height is commonplace. These versatile machinery play a vital role in construction, maintenance, warehousing, and many more sectors, offering an efficient solution for high-level tasks.
This blog post will delve into the world of MEWPs, starting with a fundamental question: “What is a MEWP?” From there, we will explore the different types of MEWPs, each tailored to meet specific work requirements. Next, we will highlight the potential hazards of using these platforms – because being forewarned is forearmed. Finally, we will lay down various safety rules and control measures essential for maintaining a safe working environment around MEWPs.
Whether you’re an experienced operator, a safety officer, or someone new to the field, the knowledge you’ll gain from this comprehensive guide will be invaluable for ensuring safety and efficiency when working with Mobile Elevating Work Platforms. Buckle up as we embark on this informative journey!
What is a MEWP?
A Mobile Elevating Work Platform (MEWP) is a type of versatile and movable machinery specially designed for safely lifting people and equipment to specific heights to perform tasks. This machinery is primarily utilized in fields like construction, maintenance, and cleaning, where jobs frequently require working at elevated levels.
At its core, a MEWP consists of three fundamental components:
- First, a work platform is equipped with controls, serving as the area where the worker stands and operates the machinery. This platform is crucial for providing a stable and secure surface for the worker, even at substantial heights.
- The second component is the extending structure, sometimes called the “lift mechanism.” A scissor mechanism, boom, or mast allows the platform to rise to the necessary height. It’s designed to offer a wide range of motion, making it possible to reach various heights and, in some cases, different lateral positions.
- Finally, the chassis is the base of the MEWP, providing stability and mobility to the entire structure. It often includes wheels or tracks, enabling the machinery to be easily moved to different locations on a job site.
Importantly, a MEWP’s design intention is that people are meant to enter and exit the work platform only from designated access points at ground level or on the chassis itself. This safety measure is designed to prevent accidents caused by improper mounting or dismounting at unsafe heights.
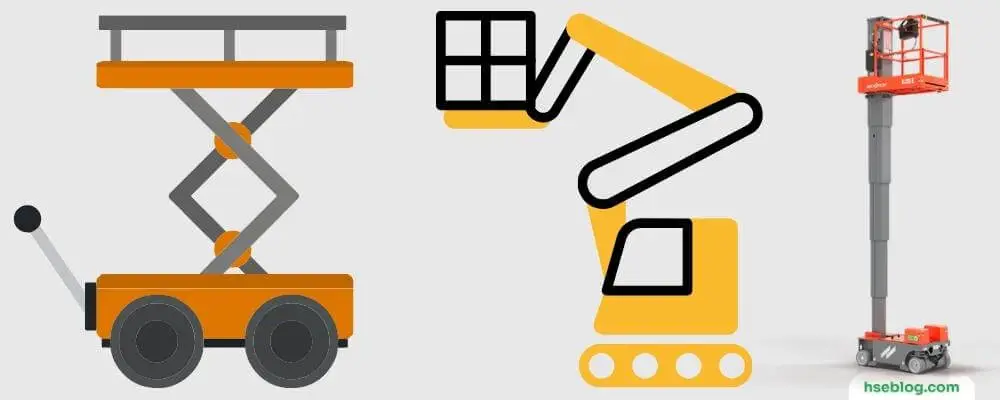
Types Of MEWPs (Mobile Elevating Work Platforms)
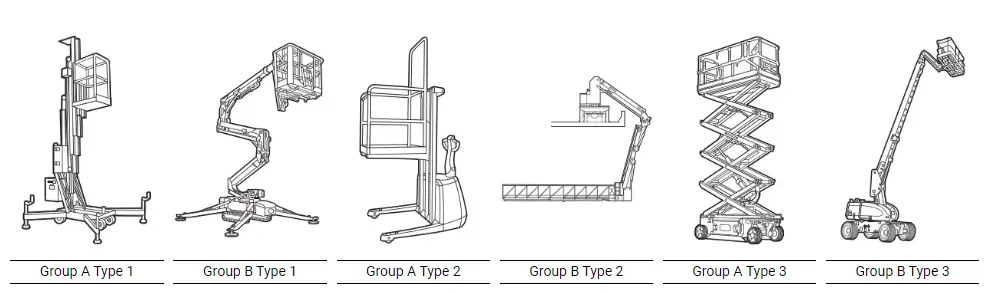
Mobile Elevating Work Platforms (MEWPs) come in various types, each designed for specific tasks or working environments. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of each type will help you choose the right platform for your needs. Here are the main types of MEWPs:
1. Scissor Lifts
Scissor lifts offer a versatile solution for tasks that require a significant amount of vertical elevation, supporting multiple workers and their tools on a large platform. Powered by hydraulics, the lift’s signature crisscrossing metal supports extend and contract to raise and lower the platform, hence the “scissor” lift. They are best suited for tasks such as ceiling repair, electrical installation, and other maintenance work requiring stable, vertical elevation. Typically, scissor lifts are used indoors on flat surfaces, though rugged, outdoor models are also available for uneven terrains.
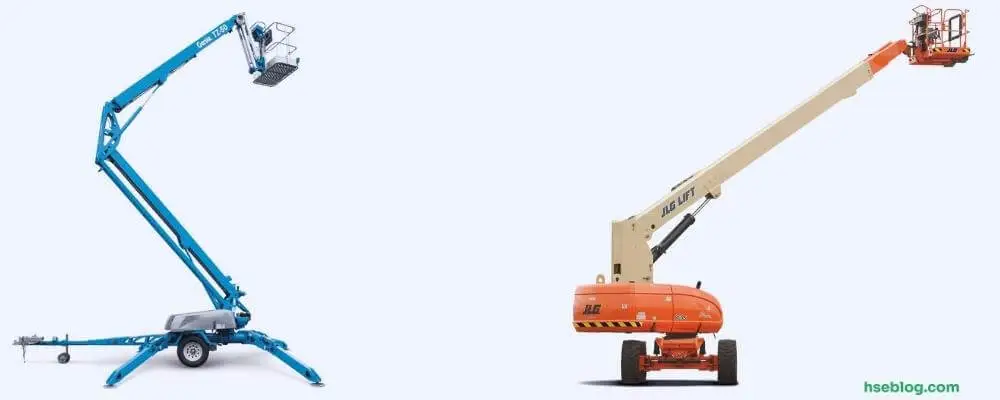
2. Boom Lifts (Cherry Pickers)
A boom lift, also known as a cherry picker due to its use in orchards, is a type of MEWP that offers vertical and horizontal reach, providing flexibility to access hard-to-reach places. The lift consists of a bucket or small platform on the end of a hydraulic mast mounted on a grounded base. Extending the boom in various directions makes this type ideal for construction, exterior painting, tree trimming, and overhead utility work. Some models can even operate on rough terrain and uneven surfaces.
3. Vertical Mast Lifts
Vertical mast lifts, also known as vertical personnel lifts, specialize in providing straight vertical access, making them perfect for tight, congested spaces or aisles. These lifts are compact, easy to maneuver, and often used in retail and warehouse settings for stock picking and routine maintenance tasks. Although their platform is typically smaller than that of scissor lifts, their compact size makes them highly beneficial in confined spaces.
4. Trailer Mounted Lifts
These lifts are built onto a towable trailer for easy transportation from one job site to another. The work platform can be raised or lowered to various heights, and the outriggers can be extended for stability during operation. This flexibility makes trailer-mounted lifts ideal for contractors who need to perform work at multiple locations. They are suitable for exterior cleaning, tree cutting, installation, and repair.
5. Spider Lifts
Spider lifts are unique because they feature four stabilizing legs, which can be extended like a spider spreading its legs. This design provides excellent stability, especially on uneven or sloped terrains. They’re lightweight and compact, coupled with their ability to traverse difficult terrain, making them a preferred choice for outdoor work, such as tree surgery, window cleaning, or maintenance work on buildings with complex architectures.
6. Telescopic Boom Lifts
Telescopic boom lifts, also known as stick booms, offer the greatest horizontal and vertical reach compared to other MEWPs. These lifts have a long, straight arm extending to substantial heights, providing unobstructed access to elevated work areas. This ability to “reach out” is invaluable for tasks that require the worker to access areas over obstacles or when working on large structures like bridges, high-rise buildings, or utility towers.

Mobile Elevating Work Platforms (MEWPs) Hazards
There are a variety of potential hazards associated with the use of Mobile Elevating Work Platforms (MEWPs). Here are ten of the most common:
- Falls from Height: Despite the safety features of MEWPs, falls from height persist as a leading cause of fatal and serious injuries within the construction industry. Workers might develop a false sense of security while elevated, prompting them to engage in risky behaviors such as leaning over the edge or not using harnesses. It’s crucial to constantly remind workers of the risks and ensure safety measures are followed consistently.
- Inadequate Training: Lack of sufficient training is another key factor contributing to accidents involving MEWPs. Operators must be well-versed in operating the equipment, understanding the potential risks, and implementing necessary safety procedures. Comprehensive training programs should be in place to ensure all users are competent and confident in managing MEWPs.
- Poor Maintenance: Accidents often stem from poor maintenance of equipment. Regular servicing and inspections can identify potential faults or weaknesses in the MEWP, ensuring they are rectified before serious incidents occur. A regular maintenance schedule based on manufacturer recommendations is essential for safe MEWP operation.
- Faulty Equipment: Similarly, equipment that’s already damaged can pose a significant danger. Broken controls, compromised structural elements, or faulty safety mechanisms can lead to malfunctions or sudden equipment failures. Prompt repair and maintenance when problems are identified can avert such risks.
- Adverse Weather Conditions: Weather plays a significant role in the safety of MEWP operations. Rain, snow, ice, or high winds can impair visibility, make surfaces slippery, and affect the stability and maneuverability of MEWPs. Workers should be trained to evaluate weather conditions and postpone operations if conditions are deemed too hazardous.
- Working in Dark Conditions: Working at night or in dimly lit conditions can increase the risk due to limited visibility. Proper lighting should be used to illuminate work areas, and reflective clothing should be worn by workers to increase visibility. Taking extra precautions when operating MEWPs in these conditions is also important.
- Proximity to Live Electrical Cables: Operating a MEWP near live electrical cables is highly hazardous. An inadvertent contact or even proximity to these cables can cause electrocution. Strict rules should be in place to maintain safe distances from electrical hazards during MEWP operations.
- Collision with Overhead Obstacles: Striking overhead objects is a common accident involving MEWPs. Workers must know their surroundings, including potential overhead hazards such as beams, pipes, or electrical cables. A thorough job site survey and planning can help identify and mitigate these risks.
- Overloading the MEWP: Overloading the MEWP beyond its specified load limit can lead to instability and potential tipping. It’s crucial to adhere to the MEWP’s safe working load limit, considering the weight of workers, tools, and materials.
- Ignoring Manufacturer’s Instructions: Ignoring the manufacturer’s safety procedures and operating instructions can lead to misuse of the MEWP and resultant accidents. Operators should always follow the manufacturer’s guidance for safe operation. If there is any doubt or uncertainty, seeking expert advice before proceeding with the operation is advisable.

Mobile Elevating Work Platforms (MEWPs) Control Measures
MEWPs are suitable for high-level work, such as changing light bulbs in a warehouse. The following factors must be considered when using a MEWP:
- Regular Maintenance and Inspection: A fundamental control measure for MEWPs is regular maintenance and inspection. This ensures the machine is in good working condition and safe to use. Maintaining a valid Certificate of Thorough Inspection, issued within the last six months, is critical for the MEWP in use. Additionally, it’s essential to establish clear procedures to follow in case of machine failure, detailing steps for safely descending and evacuating the platform.
- Trained Operators: Only fully trained and competent individuals should be allowed to operate a MEWP. This includes understanding how to control the MEWP and knowing the potential risks and necessary safety measures. Regular refresher training is beneficial to ensure operators stay updated with the latest safety protocols.
- Movement Restrictions: A crucial safety rule for MEWPs is that they should never be moved in an elevated position. This prevents the risk of tipping over or colliding with overhead structures. The platform should be fully lowered before the machine is relocated.
- Stable Ground and Load Distribution: MEWPs must be operated on level, stable ground, considering the loading capacity of floors in indoor environments. Before deployment, it’s essential to evaluate the ground conditions and the overall load the MEWP will place on the floor or ground, including its weight and the weight of workers and equipment.
- Properly Inflated Tires and Wheel Immobilization: Ensuring inflated tires is important for stability and maneuverability. When the MEWP is stationary and in use, the wheels should be immobilized to prevent unintentional movement, especially on slopes.
- Outrigger Use: When outriggers are available on the MEWP, they should be fully extended and locked in position to improve the machine’s stability during operation.
- Awareness of Overhead Hazards and Weather Conditions: Operators should be vigilant to overhead power supplies, obstructions, and adverse weather conditions. Precautions should be taken to avoid these hazards and potentially suspend operations when weather conditions pose a risk.
- Warning Signs and Barriers: Erecting warning signs and barriers around the operational area can help prevent accidental collisions with pedestrians or vehicles. It can also demarcate a safe distance around the MEWP, especially in high-traffic areas.
- Emergency Procedures Training: In addition to operational training, drivers of MEWPs should be well-versed in emergency procedures. This training is particularly important to cover power failure, operator incapacitation, or mechanical failure.
- Use of Safety Harnesses: All workers on MEWPs should be equipped with and know how to use safety harnesses. These personal fall arrest systems are crucial in preventing falls from height, especially when the MEWP is in use at significant elevations.

Additional Control Measures:
- MEWP Selection: Always choose the right MEWP for the task, considering height requirement, load capacity, indoor or outdoor use, and ground conditions.
- Pre-use Checks: Perform daily pre-use checks to ensure the MEWP is in good working condition before starting work.
- Communication: Maintain clear and effective communication between the operator and ground staff. This can help spot potential risks, communicate changes in the surroundings, or aid in emergencies.
- Avoid Overreaching: Operators should avoid leaning or reaching out from the platform. Overreaching can destabilize the MEWP and cause it to tip over.
- Securing Tools and Equipment: Tools and other equipment should be properly secured when elevated to prevent them from falling and causing injury to people below.
When properly implemented, these comprehensive safety control measures can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries associated with using MEWPs.
When working on a MEWP, there is a danger that the operator may become trapped against an overhead or adjacent object, preventing him/her from releasing the controls. Accidents are also caused when a MEWP is reversed into areas with poor pedestrian segregation and the driver has limited visibility. During any maneuvering operation, a dedicated bandsman should be used.
There is evidence of many severe and fatal accidents from entrapment accidents between guard rails on MEWPs and adjacent obstructions. Several serious accidents have been caused by workers trapped by overhead obstructions while the MEWP was in motion. These accidents often occur during maintenance operations. Risk assessments must be undertaken, and safe work systems must be developed for such work.
The Strategic Forum for Construction Plant Safety Group has published guidance on best practices when using MEWPs in confined overhead spaces. The guidance covers hazards, risk assessment, controls, and managers’ responsibilities.
HSE Suggestions On The Use Of MEWPs
If a MEWP is to be used, the HSE suggests that the following questions should be considered:
- Height – How high is the job from the ground?
- Application – Do you have the appropriate MEWP for the job? (If you’re not sure, check with the hirer or manufacturer)
- Conditions – What are the ground conditions like? Is there a risk of the MEWP becoming unstable or overturning?
- Operators – Are the people using the MEWP trained, competent, and fit to do so?
- Obstructions – Could the MEWP be caught on any protruding features or overhead hazards, such as steelwork, tree branches, or power lines?
- Traffic – Is there passing traffic, and if so, what must you do to prevent collisions?
- Restraint – Do you need to use either a work restraint (to prevent people from climbing out of the MEWP) or a fall arrest system (which will stop a person from hitting the ground if they fall out)? Allowing people to climb out of the basket is not normally recommended – Do you need to do this as part of the job?
- Checks – Has the MEWP been examined, inspected, and maintained as required by the manufacturer’s instructions, and have daily checks been carried out?

MEWP Training
Training for Mobile Elevating Work Platforms (MEWPs) is essential for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of operations. This specialized training prepares operators, supervisors, and other on-site staff to safely use, monitor, and maintain these machines. With thorough MEWP training, users understand how to operate these machines efficiently and mitigate any associated risks.
Several organizations and agencies offer comprehensive MEWP training programs covering various subjects. Here’s a general overview of what such a program might include:
- Theoretical Training: This covers the basics of MEWP operation, types of MEWPs, relevant health and safety legislation, and risk assessment. Participants will learn about machine controls, emergency procedures, and the importance of regular maintenance and inspections. They’ll also learn about the hazards associated with MEWPs and how to avoid them.
- Practical Training: This includes hands-on exercises where trainees learn to operate MEWPs under the supervision of a qualified instructor. Participants will get a feel for the controls and gain experience navigating the MEWP around a controlled environment. They’ll practice setting up and securing the machine, raising and lowering the platform, and responding to simulated emergencies.
- Evaluation: Participants will typically undergo an evaluation after the theoretical and practical training. This can involve a written test covering the theoretical aspects and a practical test where they must demonstrate their ability to safely and effectively operate a MEWP.
- Certification: Upon completing the training and evaluation, participants receive a certification, sometimes called a ‘license’ or ‘card.’ This certification demonstrates that the holder has received appropriate training to operate MEWPs safely.
These training programs suit various roles, including operators, supervisors, and managers. Even if not directly operating a MEWP, understanding how these machines work and the associated safety measures is valuable for anyone involved in a project where MEWPs are used.
Remember, MEWP training isn’t a one-time event. Regular refresher courses are crucial to maintain up-to-date knowledge and skills. Working safely with MEWPs is an ongoing commitment, and training is a key component of that commitment.

Conclusion
As we conclude this comprehensive guide on Mobile Elevating Work Platforms (MEWPs), it’s evident that these machines are a vital tool for tasks requiring work at height. We’ve explored the varied types of MEWPs, each designed to cater to specific work conditions and shed light on the potential hazards of their operation. Crucially, we’ve outlined a set of safety rules and control measures that, when implemented diligently, can significantly reduce these risks.
Understanding and respecting the capabilities and limitations of MEWPs is the first step in ensuring safe and efficient use. Whether it’s a scissor lift, a boom lift, or a vertical mast lift, each type has a purpose and is suited to particular circumstances. Always remember that the right choice of MEWP and proper operation and maintenance can go a long way in minimizing potential hazards.
However, the critical takeaway is that safety should be paramount when using these machines. A well-informed operator, familiar with the safety procedures and trained in hazard identification and risk mitigation, is the key to a safe working environment. Always remember to adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions, safety protocols, and local regulatory guidelines.
Our journey through MEWPs has been enlightening, underlining their importance while emphasizing safety. We hope you use this information to create a safer and more efficient working environment. After all, in the world of MEWPs, knowledge, and vigilance are the true lifelines.

